You can first log in to the homepage of the backend to view and judge based on "System Info" - "Sub Name".
If it is "PMNE". Then select the corresponding firmware versions of "PMNE", such as "SC7981PMNE-XXX", etc;
If it is "PMN". Select the corresponding firmware version of "PMN", such as "SC7981PMN-XXX".

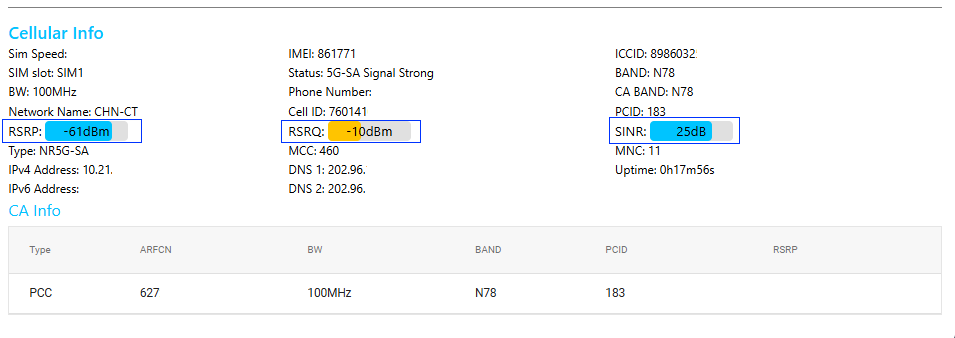
After downloading the firmware, unpack the firmware package (extract the .bin file). Then, in the product backend, go to Advance -> SYSTEM -> Upgrade firmware, import the firmware file, and click 'Update'.
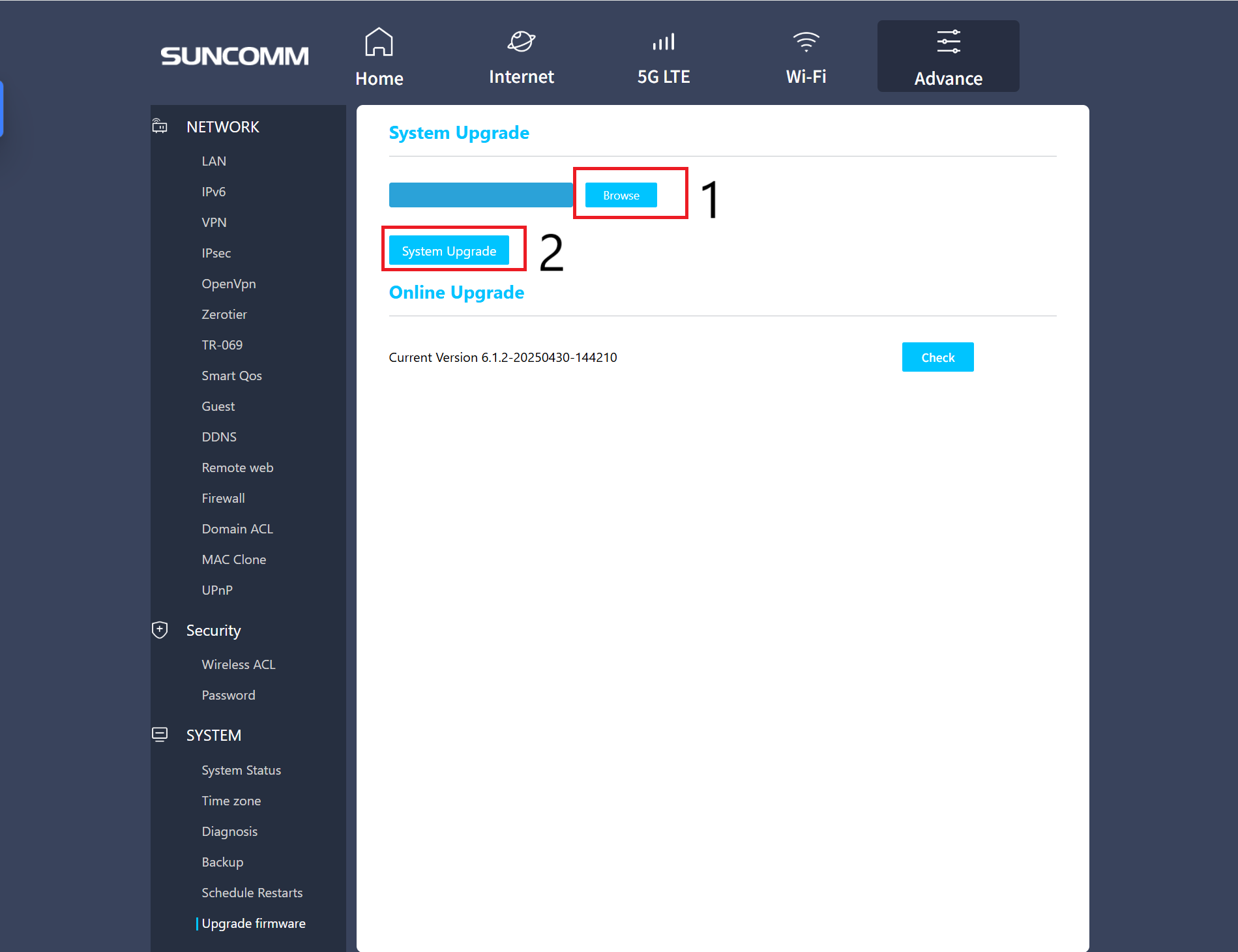
Under 5g lte go to at and then run the command: “ati” don’t include the quote marks. This is what I get back: Quectel RM520N-GL Revision: RM520NGLAAR03A04M4G revision is your firmware.
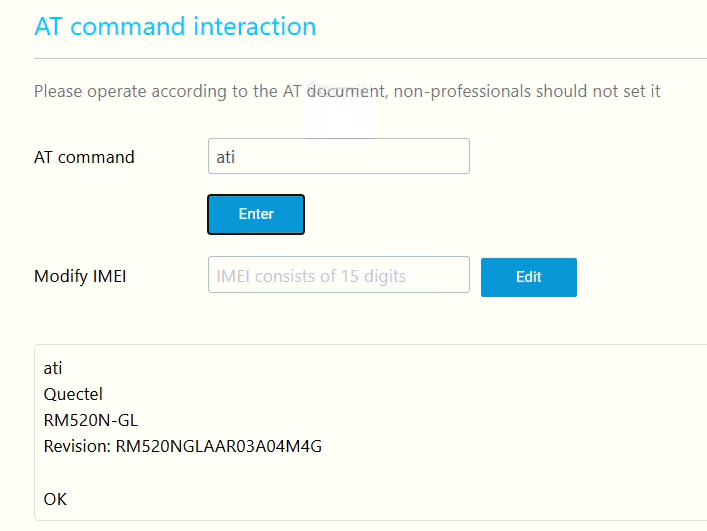
Log into the product backend, and on the homepage, you can see three values: 'RSRP', 'RSRQ', and 'SINR'.
(1) RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power): Indicates the power of the downlink reference signal received by the device, reflecting signal strength.
Excellent: -85dBm to -50dBm (strong signal, good coverage).
Fair: -95dBm to -105dBm (weak signal, may affect speed).
Poor/Very Poor: Below -105dBm (may cause disconnection).
Purpose: Used to determine base station coverage range, select the optimal base station for handover, or optimize antenna placement.
(2) RSRQ (Reference Signal Received Quality): Reflects signal quality by comparing the ratio of useful signal power to total interference and noise power (similar to signal-to-noise ratio).
Typical Range:
Excellent: -10dB to -3dB (low interference, stable transmission).
Fair: -15dB to -10dB (some interference, speed may decrease).
Poor: Below -15dB (high interference, prone to packet loss or disconnection).
Purpose: Evaluates network anti-interference capability and helps optimize network parameters or switch frequency bands.
(3) SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio): This parameter evaluates the stability of the current wireless signal in complex electromagnetic environments.
SINR > 20 dB: Signal is excellent, supporting high-bandwidth applications (e.g., 4K video).
SINR < 0 dB: Signal is severely interfered with, which may cause disconnection or high latency.
Potential Interference Sources: Can come from other routers, Bluetooth devices, microwave ovens, and other electromagnetic sources.